Magnetic pump structure and principle
A magnetic pump is a pump device that uses magnetic transmission technology to achieve liquid transportation. Its structure and principle are as follows:
Structure of a magnetic pump
The magnetic pump is mainly composed of the following parts:
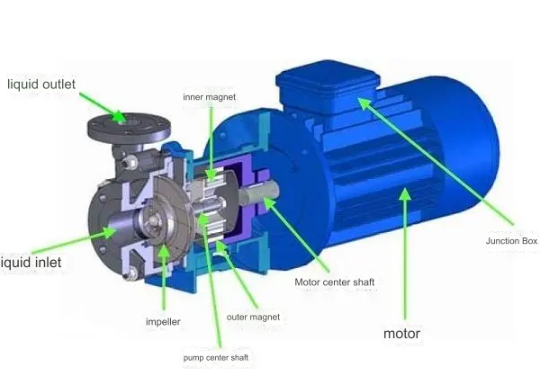
Pump body: The pump body is the main load-bearing component of the magnetic pump, usually made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, ceramics, etc. The pump body is provided with an inlet and an outlet for the suction and discharge of liquid. The pump body also includes a suction chamber and a discharge chamber. The suction chamber allows the liquid to fill the pump and reduce the pressure of the liquid, while the discharge chamber pressurizes the liquid and delivers it out.
Impeller: The impeller is located in the pump body and is the main working part of the pump. It is made of corrosion-resistant materials. When the inner magnetic shaft rotates, the impeller generates centrifugal force to achieve liquid transportation.
Inner magnetic shaft: The inner magnetic shaft is connected to the impeller and is made of permanent magnetic material. The inner magnetic shaft interacts with the outer magnetic shaft through the magnetic field to achieve synchronous rotation.
Outer magnetic shaft: The outer magnetic shaft is connected to the motor and is also made of permanent magnetic material. When the motor drives the outer magnetic shaft to rotate, the inner magnetic shaft is driven to rotate through the magnetic field.
Magnetic isolation sleeve: The magnetic isolation sleeve is the core component of the magnetic pump, which is used to isolate the liquid between the inner magnetic axis and the outer magnetic axis. The magnetic isolation sleeve is usually made of non-magnetic materials, such as stainless steel, ceramic, etc., to ensure the transmission of the magnetic field while preventing liquid leakage.
Motor: Provides power for the magnetic pump, generally driven by an electric motor.
Base: Used to support and fix all parts of the pump.
In addition, the magnetic pump may also include other auxiliary components, such as bearings, seals, etc., to ensure the normal operation and sealing performance of the pump.
Principle of magnetic pump
The working principle of the magnetic pump is based on the principle of magnetic coupling, and mainly includes the following steps:
Magnetic conversion: When the motor is started, the external magnet (ie, the outer magnetic axis) begins to rotate, generating a rotating magnetic field. This rotating magnetic field interacts with the internal magnet (ie, the inner magnetic axis) to form a magnetic coupling driving force.
Driving force transmission: Through magnetic coupling, the driving force is transmitted to the internal magnet. Since the inner magnetic axis is connected to the impeller, this driving force also acts on the impeller.
Impeller rotation: When the driving force is transmitted to the impeller, the impeller begins to rotate. During the rotation process, the impeller drives the liquid to rotate together, and the liquid enters the discharge chamber from the suction chamber under the action of centrifugal force.
Liquid delivery: The pressurized liquid is discharged from the discharge chamber through the outlet of the pump, completing the liquid delivery process.




