Mechanical seal principle and common problems of pumps
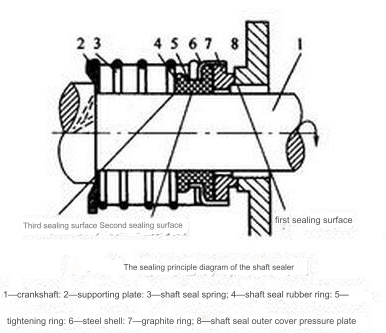
Mechanical seals are key components used in pumps to prevent leakage of working fluid along the rotating shaft. The basic principle is to form a seal by using the close fit of two planes (dynamic ring and static ring) under the action of fluid pressure and elastic force of elastic elements (such as springs). The dynamic ring is installed on the pump shaft and rotates with the shaft, while the static ring is fixed on the pump housing and remains stationary. The tiny gap between the two is maintained by a layer of flowing lubricating liquid film, which not only ensures the sealing effect but also reduces wear.
In mechanical seals, auxiliary sealing rings are also used between the static ring and the gland, the dynamic ring and the rotating shaft, and the gland and the housing to further solve the leakage problem in these parts. In addition, in order to adapt to different working conditions, mechanical seals are also divided into single-sided and double-sided, contact and non-contact, rotary and static types.
However, mechanical seals often encounter some problems during use, such as water leakage. This may be caused by wear of the dynamic and static ring surfaces, over-tight or over-loose installation, poor water quality containing particles, dry wear damage or cavitation caused by lack of water, etc. For these problems, corresponding solutions can be taken, such as adjusting the installation height, improving water quality or medium conditions, and removing air from the pipe and pump chamber.
In addition, mechanical seals also have the advantages of reliable structure, long life, no need for adjustment during operation, good vibration resistance, small power loss and wide application range. However, its structure is relatively complex, and the processing accuracy and installation technology requirements are high. It also requires certain skills and experience when disassembling and assembling. Therefore, when using and maintaining mechanical seals, special attention should be paid to their installation, adjustment and maintenance to ensure their normal operation and extend their service life.




