Volatile Solvents Pump
- Gaotian
- Shanghai
- 15days
- 1500
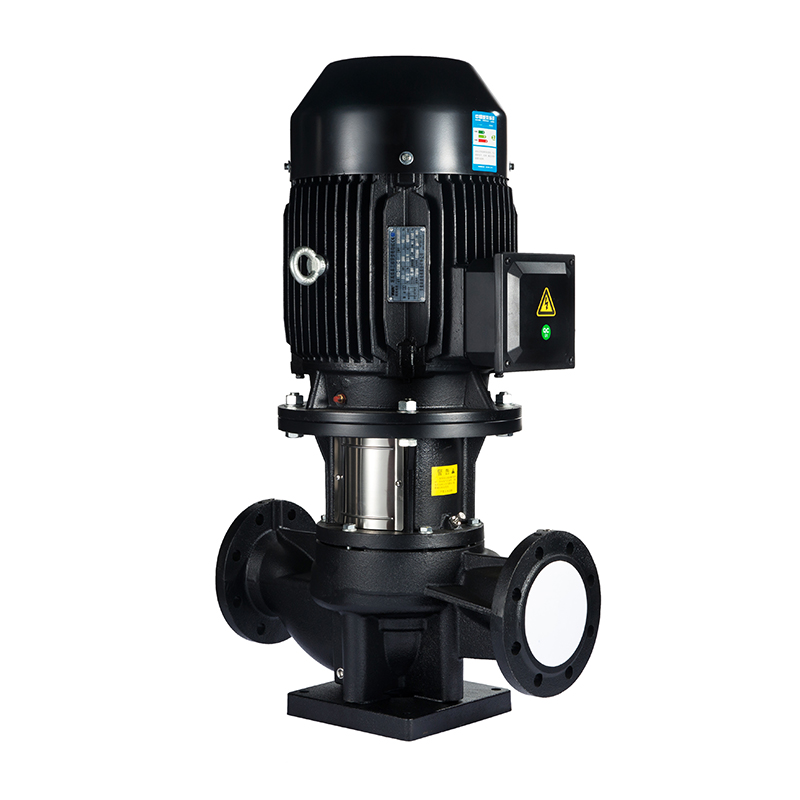
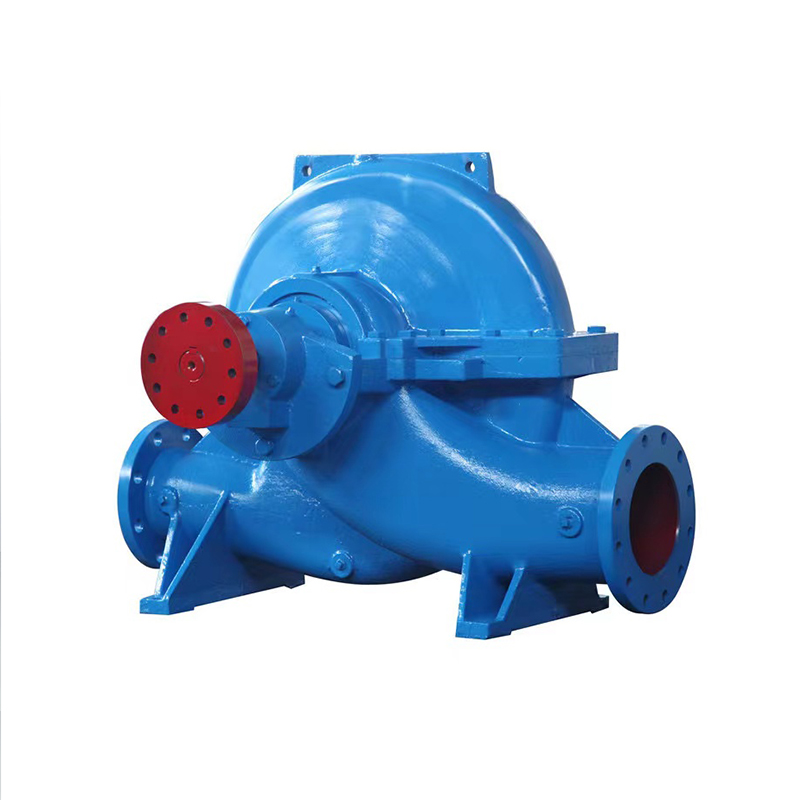
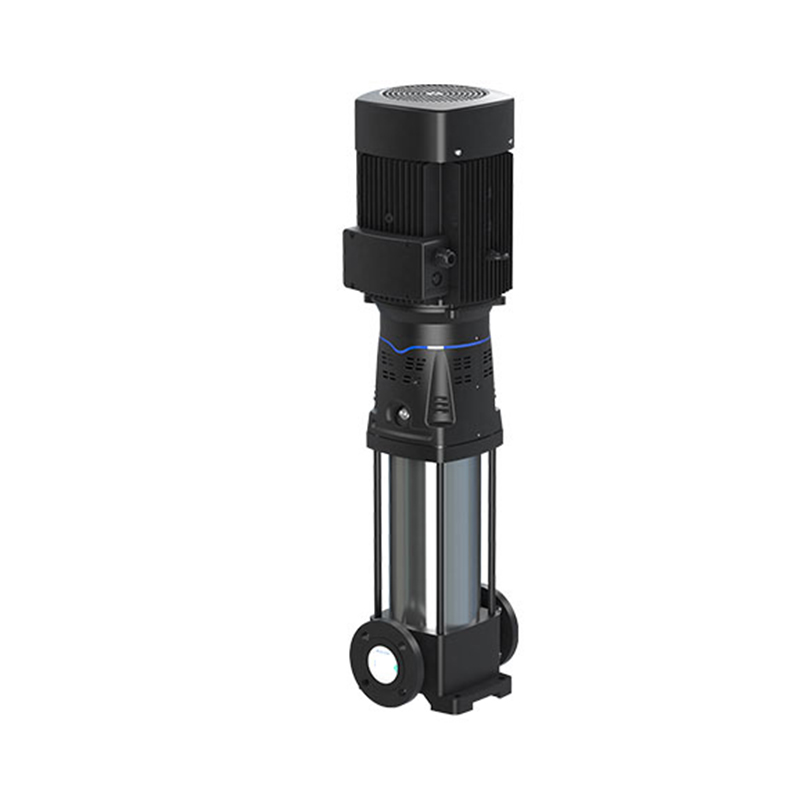
The methane pump is mainly used to transport volatile liquids and petroleum products with similar properties, such as chloromethane, liquefied petroleum gas, dimethyl ether, epoxyethane, propane, propylene, and methanol. It is especially used for the loading and unloading of chloromethane in vehicles, filling steel cylinders, and supplying ingredients in chemical workshops. The pump is a volumetric vane pump with an advanced structure. The stator surface is composed of a composite curve, and mechanical seals are used at both ends. "O"-shaped sealing rings are used on all fixed mating surfaces, and the rotating components are paired with non-metallic materials. It has the functions of reliable use and versatility.
How to Properly Connect Volatile Solvents Pump
Before using the ammonia pump, it needs to be connected to the water system. For those who may not be familiar with this aspect, we will provide a detailed introduction. The water connection of the pump involves the following two steps:
1. Connect one end of the check valve/pressure relief valve of the ammonia pump to the tap water pipe, and connect the other end to the water inlet of the water tank. Note: the outlet of the water storage tank must be connected to a section of PPR pipe of more than 1.5 meters.
2. Fill with water: Open the tap water inlet valve, and open the hot water pipe outlet. Start filling with water until the ammonia pump overflows with water, and then close the outlet tap. Check for leaks in the water storage to ensure no water leakage.
How to Properly Flush the Ammonia Pump
The mechanical seal of the ammonia pump is its main advantage. In order to extend its service life, the following are some knowledge about the flushing method of the equipment, and we hope everyone will read it carefully.
Internal flushing:
(1) When the medium transported by the ammonia pump is clean, use this method for flushing;
(2) Lead a pipeline from the pump outlet flange to flush the flushing liquid towards the sliding bearings, lubricating the sliding bearings and carrying away the heat generated by the friction, thus contributing to cooling.














